Gas turbomachinery, including gas turbines and turbo compressors, plays a vital role in various industries such as power generation, aviation, and oil and gas. These high-speed rotating machines require robust and reliable components to ensure efficient and safe operation. Among these components, bearings have a critical role in supporting the rotating shafts, minimizing friction, and facilitating smooth operation. This article delves into the significance of bearings in gas turbomachinery, their types, and the challenges associated with their design and operation.
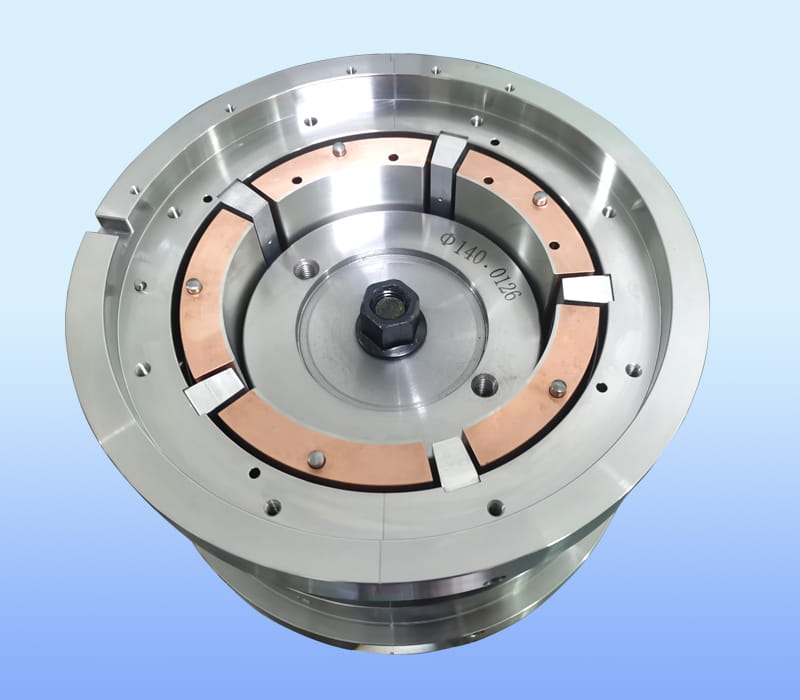
Bearings in gas turbomachinery serve multiple essential functions. Firstly, they support the rotating shafts and prevent excessive deflection, ensuring proper alignment and minimizing vibration. This, in turn, enhances the overall performance and longevity of the machine. Bearings also facilitate the transmission of loads from the rotor to the surrounding structure, preventing damage to the shaft and other components. Additionally, they enable efficient power transmission by reducing friction and dissipating heat generated during operation. Proper bearing design and selection are crucial for minimizing energy losses and maximizing the overall efficiency of the turbomachinery system.
Types of Bearings Used in Gas Turbomachinery:
Journal Bearings: Journal bearings are commonly used in gas turbines and turbo compressors. They rely on a film of lubricant between the rotating shaft and the bearing surface to reduce friction and wear. Journal bearings can be classified into hydrodynamic and hydrostatic bearings. Hydrodynamic bearings operate with the assistance of fluid pressure generated by the rotating shaft, while hydrostatic bearings utilize an external source of pressurized fluid to maintain the lubricant film.
Thrust Bearings: Thrust bearings, as the name suggests, are designed to withstand axial loads in gas turbomachinery. They prevent axial movement of the rotor and ensure its stable operation. These bearings can be classified as tilting pad, tapered land, or magnetic bearings, depending on the specific application and design requirements.
Challenges in Bearing Design and Operation:
Designing and operating bearings in gas turbomachinery pose several challenges due to the extreme operating conditions. High rotational speeds, varying loads, and elevated temperatures demand careful consideration during bearing design. Factors such as lubrication, material selection, cooling mechanisms, and bearing geometry must be optimized to ensure efficient performance and extended bearing life. Additionally, the presence of contaminants, such as dust or particulate matter in the operating environment, can impact bearing performance and require appropriate sealing measures.
Advancements in Bearing Technology:
Advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have significantly influenced bearing technology in gas turbomachinery. The use of advanced materials, such as ceramic or composite materials, can enhance bearing performance by reducing friction, increasing wear resistance, and improving high-temperature capabilities. Furthermore, the integration of sensor technologies and condition monitoring systems enables real-time monitoring of bearing health, facilitating predictive maintenance and minimizing unexpected failures.
Bearings play a critical role in gas turbomachinery by supporting rotating shafts, reducing friction, and ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Proper design, selection, and maintenance of bearings are essential for maximizing the performance, reliability, and longevity of gas turbines and turbo compressors. With ongoing advancements in bearing technology and the integration of intelligent monitoring systems, gas turbomachinery manufacturers continue to improve the efficiency and overall operation of these vital machines, contributing to a wide range of industrial applications.
